1. You performed the leopold’s maneuver and found the following: breech presentation, fetal back at the right side of the mother. Based on these findings, you can hear the fetal heart beat (PMI) BEST in which location?
A.Left lower quadrant
B.Right lower quadrant
C.Left upper quadrant
D.Right upper quadrant
Answer: (B) Right lower quadrant Right lower quadrant. The landmark to look for when looking for PMI is the location of the fetal back in relation to the right or left side of the mother and the presentation, whether cephalic or breech. The best site is the fetal back nearest the head.
2. In Leopold’s maneuver step #1, you palpated a soft broad mass that moves with the rest of the mass. The correct interpretation of this finding is:
A.The mass palpated at the fundal part is the head part.
B.The presentation is breech.
C.The mass palpated is the back
D.The mass palpated is the buttocks.
Answer: (D) The mass palpated is the buttocks. The palpated mass is the fetal buttocks since it is broad and soft and moves with the rest of the mass.
3. In Leopold’s maneuver step # 3 you palpated a hard round movable mass at the supra pubic area. The correct interpretation is that the mass palpated is:
A.The buttocks because the presentation is breech.
B.The mass palpated is the head.
C.The mass is the fetal back.
D.The mass palpated is the fetal small part
Answer: (B) The mass palpated is the head. When the mass palpated is hard round and movable, it is the fetal head.
4. The hormone responsible for a positive pregnancy test is:
A.Estrogen
B.Progesterone
C.Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
D.Follicle Stimulating hormone
Answer: (C) Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) is the hormone secreted by the chorionic villi which is the precursor of the placenta. In the early stage of pregnancy, while the placenta is not yet fully developed, the major hormone that sustains the pregnancy is HCG.
5. The hormone responsible for the maturation of the graafian follicle is:
A.Follicle stimulating hormone
B.Progesterone
C.Estrogen
D.Luteinizing hormone
Answer: (A) Follicle stimulating hormone The hormone that stimulates the maturation if the of the graafian follicle is the Follicle Stimulating Hormone which is released by the anterior pituitary gland.
7. The most common normal position of the fetus in utero is:
A.Transverse position
B.Vertical position
C.Oblique position
D.None of the above
Answer: (B) Vertical position Vertical position means the fetal spine is parallel to the maternal spine thus making it easy for the fetus to go out the birth canal. If transverse or oblique, the fetus can’t be delivered normally per vagina.
8. In the later part of the 3rd trimester, the mother may experience shortness of breath. This complaint maybe explained as:
A.A normal occurrence in pregnancy because the fetus is using more oxygen
B.The fundus of the uterus is high pushing the diaphragm upwards
C.The woman is having allergic reaction to the pregnancy and its hormones
D.The woman maybe experiencing complication of pregnancy
Answer: (B) The fundus of the uterus is high pushing the diaphragm upwards From the 32nd week of the pregnancy, the fundus of the enlarged uterus is pushing the respiratory diaphragm upwards. Thus, the lungs have reduced space for expansion consequently reducing the oxygen supply.
9. Which of the following findings in a woman would be consistent with a pregnancy of two months duration?
A.Weight gain of 6-10 lbs. and presence of striae gravidarum
B.Fullness of the breast and urinary frequency
C.Braxton Hicks contractions and quickening
D.Increased respiratory rate and ballottement
Answer: (B) Fullness of the breast and urinary frequency Fullness of the breast is due to the increased amount of progesterone in pregnancy. The urinary frequency is caused by the compression of the urinary bladder by the gravid uterus which is still within the pelvic cavity during the first trimester.
10. Which of the following is a positive sign of pregnancy?
A.Fetal movement felt by mother
B.Enlargement of the uterus
C.(+) pregnancy test
D.(+) ultrasound
Answer: (D) (+) ultrasound A positive ultrasound will definitely confirm that a woman is pregnant since the fetus in utero is directly visualized.
11. What event occurring in the second trimester helps the expectant mother to accept the pregnancy?
A.Lightening
B.Ballotment
C.Pseudocyesis
D.Quickening
Answer: (D) Quickening Quickening is the first fetal movement felt by the mother makes the woman realize that she is truly pregnant. In early pregnancy, the fetus is moving but too weak to be felt by the mother. In the 18th-20th week of gestation, the fetal movements become stronger thus the mother already feels the movements.
12. Shoes with low, broad heels, plus a good posture will prevent which prenatal discomfort?
A.Backache
B.Vertigo
C.Leg cramps
D.Nausea
Answer: (A) Backache Backache usually occurs in the lumbar area and becomes more problematic as the uterus enlarges. The pregnant woman in her third trimester usually assumes a lordotic posture to maintain balance causing an exaggeration of the lumbar curvature. Low broad heels provide the pregnant woman with a good support.
13. When a pregnant woman experiences leg cramps, the correct nursing intervention to relieve the muscle cramps is:
A.Allow the woman to exercise
B.Let the woman walk for a while
C.Let the woman lie down and dorsiflex the foot towards the knees
D.Ask the woman to raise her legs
Answer: (C) Let the woman lie down and dorsiflex the foot towards the knees Leg cramps is caused by the contraction of the gastrocnimeus (leg muscle). Thus, the intervention is to stretch the muscle by dosiflexing the foot of the affected leg towards the knee.
14. From the 33rd week of gestation till full term, a healthy mother should have prenatal check up every:
A.week
B.2 weeks
C.3 weeks
D.4 weeks
Answer: (A) week In the 9th month of pregnancy the mother needs to have a weekly visit to the prenatal clinic to monitor fetal condition and to ensure that she is adequately prepared for the impending labor and delivery.
15. The expected weight gain in a normal pregnancy during the 3rd trimester is
A.1 pound a week
B.2 pounds a week
C.10 lbs a month
D.10 lbs total weight gain in the 3rd trimester
Answer: (A) 1 pound a week During the 3rd trimester the fetus is gaining more subcutaneous fat and is growing fast in preparation for extra uterine life. Thus, one pound a week is expected.
16. In the Batholonew’s rule of 4, when the level of the fundus is midway between the umbilicus and xyphoid process the estimated age of gestation (AOG) is:
A.5th month
B.6th month
C.7th month
D.8th month
Answer: (C) 7th month In Bartholomew’s Rule of 4, the landmarks used are the symphysis pubis, umbilicus and xyphoid process. At the level of the umbilicus, the AOG is approximately 5 months and at the level of the xyphoid process 9 months. Thus, midway between these two landmarks would be considered as 7 months AOG.
17. The following are ways of determining expected date of delivery (EDD) when the LMP is unknown EXCEPT:
A.Naegele’s rule
B.Quickening
C.Mc Donald’s rule
D.Batholomew’s rule of 4
Answer: (A) Naegele’s rule Naegele’s Rule is determined based on the last menstrual period of the woman.
18. If the LMP is Jan. 30, the expected date of delivery (EDD) is
A.Oct. 7
B.Oct. 24
C.Nov. 7
D.Nov. 8
Answer: (C) Nov. 7 Based on the last menstrual period, the expected date of delivery is Nov. 7. The formula for the Naegele’s Rule is subtract 3 from the month and add 7 to the day.
19. Kegel’s exercise is done in pregnancy in order to:
A.Strengthen perineal muscles
B.Relieve backache
C.Strengthen abdominal muscles
D.Prevent leg varicosities and edema
Answer: (A) Strengthen perineal muscles Kegel’s exercise is done by contracting and relaxing the muscles surrounding the vagina and anus in order to strengthen the perineal muscles
20. Pelvic rocking is an appropriate exercise in pregnancy to relieve which discomfort?
A.Leg cramps
B.Urinary frequency
C.Orthostatic hypotension
D.Backache
Answer: (D) Backache Backache is caused by the stretching of the muscles of the lower back because of the pregnancy. Pelvic rocking is good to relieve backache.
21. The main reason for an expected increased need for iron in pregnancy is:
A.The mother may have physiologic anemia due to the increased need for red blood cell mass as well as the fetal requires about 350-400 mg of iron to grow
B.The mother may suffer anemia because of poor appetite
C.The fetus has an increased need for RBC which the mother must supply
D.The mother may have a problem of digestion because of pica
Answer: (A) The mother may have physiologic anemia due to the increased need for red blood cell mass as well as the fetal requires about 350-400 mg of iron to grow About 400 mgs of Iron is needed by the mother in order to produce more RBC mass to be able to provide the needed increase in blood supply for the fetus. Also, about 350-400 mgs of iron is need for the normal growth of the fetus. Thus, about 750-800 mgs iron supplementation is needed by the mother to meet this additional requirement.
22. The diet that is appropriate in normal pregnancy should be high in
A.Protein, minerals and vitamins
B.Carbohydrates and vitamins
C.Proteins, carbohydrates and fats
D.Fats and minerals
Answer: (A) Protein, minerals and vitamins In normal pregnancy there is a higher demand for protein (body building foods), vitamins (esp. vitamin A, B, C, folic acid) and minerals (esp. iron, calcium, phosphorous, zinc, iodine, magnesium) because of the need of the growing fetus.
24. Which of the following signs will require a mother to seek immediate medical attention?
A.When the first fetal movement is felt
B.No fetal movement is felt on the 6th month
C.Mild uterine contraction
D.Slight dyspnea on the last month of gestation
Answer: (B) No fetal movement is felt on the 6th month Fetal movement is usually felt by the mother during 4.5 – 5 months. If the pregnancy is already in its 6th month and no fetal movement is felt, the pregnancy is not normal either the fetus is already dead intra-uterine or it is an H-mole.
25. You want to perform a pelvic examination on one of your pregnant clients. You prepare your client for the procedure by:
A.Asking her to void
B.Taking her vital signs and recording the readings
C.Giving the client a perineal care
D.Doing a vaginal prep
Answer: (A) Asking her to void A pelvic examination includes abdominal palpation. If the pregnant woman has a full bladder, the manipulation may cause discomfort and accidental urination because of the pressure applied during the abdominal palpation. Also, a full bladder can impede the accuracy of the examination because the bladder (which is located in front of the uterus) can block the uterus.
26. When preparing the mother who is on her 4th month of pregnancy for abdominal ultrasound, the nurse should instruct her to:
A.Observe NPO from midnight to avoid vomiting
B.Do perineal flushing properly before the procedure
C.Drink at least 2 liters of fluid 2 hours before the procedure and not void until the procedure is done D.Void immediately before the procedure for better visualization
Answer: (C) Drink at least 2 liters of fluid 2 hours before the procedure and not void until the procedure is done Drinking at least 2 liters of water 2 hours before the procedure will result to a distended bladder. A full bladder is needed when doing an abdominal ultrasound to serve as a “window” for the ultrasonic sound waves to pass through and allow visualization of the uterus (located behind the urinary bladder).
27. The nursing intervention to relieve “morning sickness” in a pregnant woman is by giving
A.Dry carbohydrate food like crackers
B.Low sodium diet
C.Intravenous infusion
D.Antacid
Answer: (A) Dry carbohydrate food like crackers Morning sickness maybe caused by hypoglycemia early in the morning thus giving carbohydrate food will help.
28. The common normal site of nidation/implantation in the uterus is
A.Upper uterine portion
B.Mid-uterine area
C.Lower uterine segment
D.Lower cervical segment
Answer: (A) Upper uterine portion The embryo’s normal nidation site is the upper portion of the uterus. If the implantation is in the lower segment, this is an abnormal condition called placenta previa.
29. Mrs. Santos is on her 5th pregnancy and has a history of abortion in the 4th pregnancy and the first pregnancy was a twin. She is considered to be
A.G 4 P 3
B.G 5 P 3
C.G 5 P 4
D.G 4 P 4
Answer: (B) G 5 P 3 Gravida refers to the total number of pregnancies including the current one. Para refers to the number of pregnancies that have reached viability. Thus, if the woman has had one abortion, she would be considered Para 3. Twin pregnancy is counted only as 1.
30. The following are skin changes in pregnancy EXCEPT:
A.Chloasma
B.Striae gravidarum
C.Linea negra
D.Chadwick's sign
Answer: (D) Chadwick's sign Chadwick's sign is bluish discoloration of the vaginal mucosa as a result of the increased vascularization in the area.
31. Which of the following statements is TRUE of conception?
A.Within 2-4 hours after intercourse conception is possible in a fertile woman
B.Generally, fertilization is possible 4 days after ovulation
C.Conception is possible during menstruation in a long menstrual cycle
D.To avoid conception, intercourse must be avoided 5 days before and 3 days after menstruation
Answer: (A) Within 2-4 hours after intercourse conception is possible in a fertile woman The sperms when deposited near the cervical os will be able to reach the fallopian tubes within 4 hours. If the woman has just ovulated (within 24hours after the rupture of the graafian follicle), fertilization is possible.
32. Which of the following are the functions of amniotic fluid? 1.Cushions the fetus from abdominal trauma 2.Serves as the fluid for the fetus 3.Maintains the internal temperature 4.Facilitates fetal movement
A.1 & 3
B.1, 3, 4
C.1, 2, 3
D.All of the above
Answer: (D) All of the above All the four functions enumerated are true of amniotic fluid.
33. You are performing abdominal exam on a 9th month pregnant woman. While lying supine, she felt breathless, had pallor, tachycardia, and cold clammy skin. The correct assessment of the woman’s condition is that she is
A.Experiencing the beginning of labor
B.Having supine hypotension
C.Having sudden elevation of BP
D.Going into shock
Answer: (B) Having supine hypotension Supine hypotension is characterized by breathlessness, pallor, tachycardia and cold clammy skin. This is due to the compression of the abdominal aorta by the gravid uterus when the woman is on a supine position.
34. Smoking is contraindicated in pregnancy because
A.Nicotine causes vasodilation of the mother’s blood vessels
B.Carbon monoxide binds with the hemoglobin of the mother reducing available hemoglobin for the fetus
C.The smoke will make the fetus and the mother feel dizzy
D.Nicotine will cause vasoconstriction of the fetal blood vessels
Answer: (B) Carbon monoxide binds with the hemoglobin of the mother reducing available hemoglobin for the fetus Carbon monoxide is one of the substances found in cigarette smoke. This substance diminishes the ability of the hemoglobin to bind with oxygen thus reducing the amount of oxygenated blood reaching the fetus.
35. Which of the following is the most likely effect on the fetus if the woman is severely anemic during pregnancy?
A.Large for gestational age (LGA) fetus
B.Hemorrhage
C.Small for gestational age (SGA) baby
D.Erythroblastosis fetalis
Answer: (C) Small for gestational age (SGA) baby Anemia is a condition where there is a reduced amount of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is needed to supply the fetus with adequate oxygen. Oxygen is needed for normal growth and development of the fetus.
36. Which of the following signs and symptoms will most likely make the nurse suspect that the patient is having hydatidiform mole?
A.Slight bleeding
B.Passage of clear vesicular mass per vagina
C.Absence of fetal heart beat
D.Enlargement of the uterus
Answer: (B) Passage of clear vesicular mass per vagina Hydatidiform mole (H-mole) is characterized by the degeneration of the chorionic villi wherein the villi becomes vesicle-like. These vesicle-like substances when expelled per vagina and is a definite sign that the woman has H-mole.
37. Upon assessment the nurse found the following: fundus at 2 fingerbreadths above the umbilicus, last menstrual period (LMP) 5 months ago, fetal heart beat (FHB) not appreciated. Which of the following is the most possible diagnosis of this condition?
A.Hydatidiform mole
B.Missed abortion
C.Pelvic inflammatory disease
D.Ectopic pregnancy
Answer: (A) Hydatidiform mole Hydatidiform mole begins as a pregnancy but early in the development of the embryo degeneration occurs. The proliferation of the vesicle-like substances is rapid causing the uterus to enlarge bigger than the expected size based on ages of gestation (AOG). In the situation given, the pregnancy is only 5 months but the size of the uterus is already above the umbilicus which is compatible with 7 months AOG. Also, no fetal heart beat is appreciated because the pregnancy degenerated thus there is no appreciable fetal heart beat.
38. When a pregnant woman goes into a convulsive seizure, the MOST immediate action of the nurse to ensure safety of the patient is:
A.Apply restraint so that the patient will not fall out of bed
B.Put a mouth gag so that the patient will not bite her tongue and the tongue will not fall back
C.Position the mother on her side to allow the secretions to drain from her mouth and prevent aspiration
D.Check if the woman is also having a precipitate labor
Answer: (C) Position the mother on her side to allow the secretions to drain from her mouth and prevent aspiration Positioning the mother on her side will allow the secretions that may accumulate in her mouth to drain by gravity thus preventing aspiration pneumonia. Putting a mouth gag is not safe since during the convulsive seizure the jaw will immediately lock. The mother may go into labor also during the seizure but the immediate concern of the nurse is the safety of the baby. After the seizure, check the perineum for signs of precipitate labor.
39. A gravido-cardiac mother is advised to observe bedrest primarily to
A.Allow the fetus to achieve normal intrauterine growth
B.Minimize oxygen consumption which can aggravate the condition of the compromised heart of the mother
C.Prevent perinatal infection
D.Reduce incidence of premature labor
Answer: (B) Minimize oxygen consumption which can aggravate the condition of the compromised heart of the mother Activity of the mother will require more oxygen consumption. Since the heart of a gravido-cardiac is compromised, there is a need to put a mother on bedrest to reduce the need for oxygen.
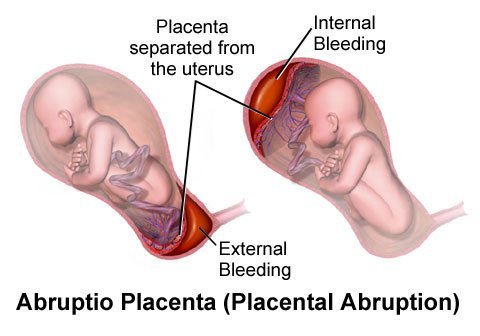
40. A pregnant mother is admitted to the hospital with the chief complaint of profuse vaginal bleeding, AOG 36 wks, not in labor. The nurse must always consider which of the following precautions:
A.The internal exam is done only at the delivery under strict asepsis with a double set-up
B.The preferred manner of delivering the baby is vaginal
C.An emergency delivery set for vaginal delivery must be made ready before examining the patient D.Internal exam must be done following routine procedure
Answer: (A) The internal exam is done only at the delivery under strict asepsis with a double set-up Painless vaginal bleeding during the third trimester maybe a sign of placenta praevia. If internal examination is done in this kind of condition, this can lead to even more bleeding and may require immediate delivery of the baby by cesarean section. If the bleeding is due to soft tissue injury in the birth canal, immediate vaginal delivery may still be possible so the set up for vaginal delivery will be used. A double set-up means there is a set up for cesarean section and a set-up for vaginal delivery to accommodate immediately the necessary type of delivery needed. In both cases, strict asepsis must be observed.
 CLICK THIS ICON BELOW TO ZOOM
CLICK THIS ICON BELOW TO ZOOM